 Polymath and Renaissance guy Sir Francis Galton published an article in the journal Nature by the title of "Visualized Numerals."
Polymath and Renaissance guy Sir Francis Galton published an article in the journal Nature by the title of "Visualized Numerals."The year in which he did so was 1880.
Now, hold it right there. When you read that last sentence, what image formed in your mind to represent that piece of information? "The year in which he did so was 1880." I suppose one could visualize a copy of the journal with the article in it and at the same time a calendar on the wall that says "1880." That would be quite logical, but it's not how I see it. I see rather a sort of chart of the centuries laid out, and in a certain spot late in the 1800's is a little image of Sir Francis Galton writing his article.
(If you need to know what he looks like in order to form such an image, there is a very nice picture of him at http://www.galton.org/, but take my word for it--he looks exactly like someone named "Sir Francis Galton" ought to look.)
Here's my point: you might expect that my mental chart of the centuries simply consists of one after the other, but it isn't quite like that. It has a few peculiarities. All the centuries from antiquity to the 20th century are laid out in a series running from right to left. Each is a rectangle something like a page of a book. Within each century, the years run from bottom to top (with a few zigs and zags of their own). But, for no particular reason that I can tell, the 21st century sits on top of the 20th century rather than to the right, and the 22nd and successive centuries are then laid out to the left of the 21st. So, for example, when I read the end of The Time Machine, when the Earth in the far future is inhabited by giant crabs, I picture this happening way out to the left of the diagram.
In the distant past, somewhere beyond the beginning of history, the pages blur into a time line. Somewhere around the emergence of Homo Sapiens, the line makes a bend so that one is heading upwards in order to go back in time. The line is populated with images of the animals that existed in any given era. During the Age of Dinosaurs, the primitive mammals are running along a smaller timeline to the left of the main time line.
The line extends up until about 4 billion years ago and then takes another bend so that again one is heading rightwards in order to go back in time. This part of the line is populated with vague images of galaxies and nebulae until it runs up against a hemispherical cul-de-sac, which is my mental image of the Big Bang (the universe closing down [as time runs backwards] to a point).
This image has been my mental map for the flow of time since a very young age. I'm quite sure no one else's is quite the same. But does everybody else even have a map? From time to time I have tried asking others how they visualize the flow of time, but usually can't get much of an answer. I've never been sure whether this is because they have some fundamentally different mental mechanism at work, or they are just not good enough at introspective thinking.
That's why I was so fascinated to find this article. It concerns the visualization of numbers rather than the flow of time (I use a different mental map for numbers, still another for the months of the year), but the essential concept is the same. The article includes several interesting diagrams of the mental number maps of various individuals. One is above. Here are a couple more:
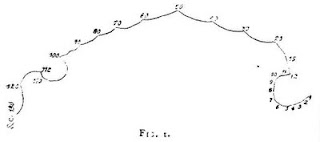
 This has the same fascination as those idle thoughts you have: "I wonder if everyone else sees the same color red as I do?" Well, maybe not you--I find that certain people never think about such things. Here is a similar issue, except in this case you can find that what different people "see" is very different.
This has the same fascination as those idle thoughts you have: "I wonder if everyone else sees the same color red as I do?" Well, maybe not you--I find that certain people never think about such things. Here is a similar issue, except in this case you can find that what different people "see" is very different.These diagrams are called "number forms." For some reason they are often discussed in connection with synaesthesia, which is a cross-linkage between different senses--experiencing colors as sounds, for example. (See, for example, the Wikipedia article on "Number forms.") I have no such tendencies that I am aware of.
Galton pursued an introspective, subjective type of psychology that seems to have gone out of style. His interests extended far beyond this: "geographer, meteorologist, tropical explorer, founder of differential psychology, inventor of fingerprint identification, pioneer of statistical correlation and regression, convinced hereditarian, eugenicist, proto-geneticist, half-cousin of Charles Darwin and best-selling author", according to http://www.galton.org/. I recommend perusing their publication list.




No comments:
Post a Comment